Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Should You Know About the Monkeypox Vaccine?
Monkeypox might seem like a virus right out of the pages of a comic book, but it is a bona fide viral illness that has made headlines in recent years. Ever since the world became more acquainted with it, thanks to good old global health alerts, the monkeypox virus and the disease it causes have become popular conversational pieces among medical practitioners and laypeople alike. Here’s everything you need to know about monkeypox—its symptoms and yes, most especially, information on getting that sweet monkeypox vaccine.
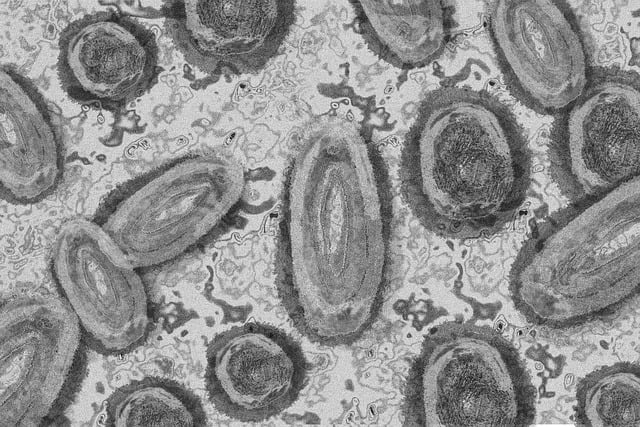
What Exactly Is Monkeypox, and How Does It Spread?
Monkeypox is an extremely rare viral disease caused by—you guessed it!—the monkeypox virus. It is classified under the Orthopoxvirus genus (like its distant cousin variola virus—the notorious smallpox triggerer). Despite its name suggesting that only monkeys are at risk, Homo sapiens may contract this disease through other routes as well. The transmission usually occurs in rainforest-dwelling communities of Central and West Africa where animals like rodents and primates harbor the virus.
The monkeypox virus spreads from animals to humans through contact with the animal’s blood or other bodily fluids, an infected animal bite or scratch, being killed and preparing/eating bushmeat, or if a person comes into contact with an item that has been contaminated by a sick animal (such as bedding). After human infection has occurred, human-to-human transmission can occur either through respiratory droplets in close face-to-face contact during the 1st week of illness or via contact with blood, body fluids/excretions, or skin lesions of an ill person; objects used by someone infected with monkeypox can also be contagious.
What Are the Symptoms of Monkeypox?
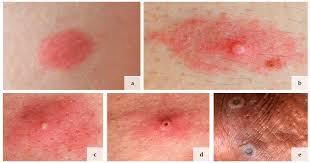
Monkeypox start similar to other viral illnesses; therefore early diagnosis is difficult without laboratory confirmation. Symptoms include:
Fever: One of the initial monkeypox symptoms is usually fever, along with chills.
Headache: During the early stages, most patients are plagued by constant headache which can be severe.
Muscle Aches: Are similar to the flu. They can be all over and bad.
Exhaustion: A general feeling of tiredness that doesn’t go away with rest.
Swollen Lymph Nodes: This is a key symptom that differentiates monkeypox from smallpox.
After 1 to 3 days of the onset of fever, a rash starts developing. It first appears on the face then spreads to other parts of the body. Eventually, it develops into raised bumps that fill with fluid and later scab over and fall off. The rash can be painful, itchy and usually disfiguring especially if not properly managed.
The severity of monkeypox symptoms differs from person to person. Some may have a mild illness while others may be more severe especially if they have certain conditions that weaken their immune system.
Why Is the Monkeypox Vaccine Important?
Because monkeypox can cause severe disease and is spread between humans, the vaccine is a very important tool to prevent outbreaks. It is especially important for people at high risk of infection – such as healthcare workers, laboratory workers handling specimens or animals linked to monkeypox, and people who live in or travel to areas where the virus is found – to be vaccinated.
The monkeypox vaccine is safe and produces a good immune response, which provides protection from monkeypox for most people. The goal of the vaccination strategy during an outbreak is to stop the virus transmission in affected communities so fewer people become ill.
Healthcare Workers: People who take care of patients with monkeypox or work in a laboratory where the virus is kept.
Laboratory Workers: People that handle specimens potentially containing monkeypox virus.
People in Endemic Areas: Persons who live in or travel to areas where monkeypox is reported commonly.
Close Contacts of Infected People: Anyone who has been in close contact with someone infected with the monkeypox virus.
Be sure to consult a health care provider about your specific situation and the vaccine’s possible benefits and side effects.
How Good Is Monkeypox Vaccine?
The monkeypox vaccine has been tested in many studies and no vaccine is 100% effective but the monkeypox vaccine works very well at preventing the disease. People who get the vaccine are much less likely to develop monkeypox and if they do, they generally have milder illness and shorter duration of symptoms.
It is important to note that the monkeypox vaccine is actually made from the smallpox vaccine, which we used to eradicate smallpox from the planet. Since monkeypox and variola (small pox) viruses are so similar, the monkeypox vaccine has been an effective way to stop the spread of this virus.
Are There Side Effects From The Monkey Pox Vaccine?
Like all vaccines, monkeypox vaccine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Side effects are usually mild and go away on their own. Reactions such as soreness at the injection site can happen after administration of any dose of monkeypox vaccine. The following is a list of possible side effects that may occur from monkeypox vaccine. This is not a comprehensive list. These side-effects are possible, but do not always occur. Some of the side-effects may be rare but serious.
Soreness at the Injection Site: Soreness at the injection site can happen after administration of any dose of monkeypox vaccine.
Redness at the Injection Site: Redness at the injection site can happen after administration of any dose of monkeypox vaccine.
Swelling or Hardening at the Injection Site: Swelling and hardening or lumping in one area happens very rarely with small-scale (dose) reactions to living vaccines and in most cases resolves on its own within 1-6 months, without complications.
Muscle Aches: Muscle aches can also be a symptom linked to an immune defence reaction by your body.
Mild Fever: Some people develop a low grade fever after the vaccination.
Fatigue: Feeling tired or sluggish for a day or two is not uncommon.
Headache: You may develop a mild headache, much like what you would experience following other immunizations.
Serious side effects are extremely rare. Like any medicine, this vaccine can cause serious problems, such as severe allergic reactions. If you have any unusual symptoms after vaccination, call your healthcare professional right away.
What Are the Challenges in Controlling Monkeypox?

Despite availability of monkeypox vaccine, there are several challenges faced in controlling the spread of monkeypox. These include:
Limited Access to Vaccines: In some parts of the world, particularly in developing countries, the monkeypox vaccine is in short supply. This makes it difficult to effectively target those populations that are most at risk.
Public Awareness: Many people are simply not aware of either the dangers associated with monkeypox or that there even exists a vaccine for this virus. Public informational campaigns are needed to both raise awareness and further increase vaccination rates.
Logistics and Infrastructure: The delivery of vaccines to remote or underserved areas may require considerable resources and coordination. Globally, concerted attempts are being made to tackle these issues, but ongoing awareness and support from the international community is required.
Global work is being done to help these global challenges, but we need the ongoing care and support of the global community.
What to do if you think you have monkeypox?
If you develop symptoms that suggest monkeypox and have been in contact with a person or animal known or suspected to have monkeypox, or if you have traveled to an area where monkeypox occurs, visit your healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment help prevent the virus from spreading as well as help make the symptoms less severe.
But let me show you how all of these health articles I’ve written are connected and really should be looked at under the same umbrella. “Is Pneumonia Contagious?“ AND “Is Walking Pneumonia Contagious?“ both give some good knowledge on respiratory health. You can also learn even more when looking at how viral infections work in general with “Virus“, or by looking at one that is even more unique to handle like “HIV.” All of this knowledge just makes us better understand how things affecting our respiratory health, whether as simple as a common infection, or complex like HIV,, impacts our overall well-being! It’s so important to stay up-to-date because every little bit helps!
Frequently Asked Questions:
Can the monkeypox vaccine prevent other diseases?
Is the monkeypox vaccine safe for pregnant women?
The safety of taking this vaccine while pregnant hasn’t been widely studied so pregnant women should speak to their doctor or healthcare provider more about this.
